Page 28 - Industrial Plants 2014
P. 28
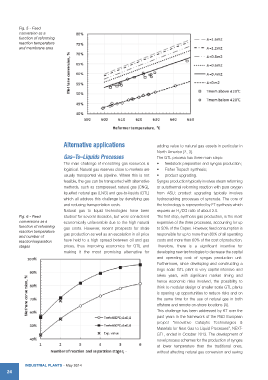
Fig. 5 - Feed
conversion as a
function of reforming
reaction temperature
and membrane area
Alternative applications adding value to natural gas assets in particular in
North America [2, 3].
Gas–To–Liquids Processes The GTL process has three main steps:
The main challenge of monetizing gas resources is • feedstock preparation and syngas production;
logistical. Natural gas reserves close to markets are • Fisher Tropsch synthesis;
usually transported via pipeline. Where this is not • product upgrading.
feasible, the gas can be transported with alternative Syngas production typically involves steam reforming
methods, such as compressed natural gas (CNG), or autothermal reforming reaction with pure oxygen
liquefied natural gas (LNG) and gas-to-liquids (GTL) from ASU; product upgrading typically involves
which all address this challenge by densifying gas hydrocracking processes of syncrude. The core of
and reducing transportation costs. the technology is represented by FT synthesis which
Natural gas to liquid technologies have been requires an H /CO ratio of about 2.0.
2
Fig. 6 - Feed studied for several decades, but were considered The first step, synthesis gas production, is the most
conversions as a economically unfavorable due to the high natural expensive of the three processes, accounting for up
function of reforming gas costs. However, recent prospects for shale to 50% of the Capex. However, feed consumption is
reaction temperature
and number of gas production as well as an escalation in oil price responsible for up to more than 80% of all operating
reaction/separation have held to a high spread between oil and gas costs and more than 60% of the cost of production.
stages prices, thus improving economics for GTL and Therefore, there is a significant incentive for
making it the most promising alternative for developing new technologies to decrease the capital
and operating cost of syngas production unit.
Furthermore, since developing and constructing a
large scale GTL plant is very capital intensive and
takes years, with significant market timing and
hence economic risks involved, the possibility to
think to modular design of smaller scale GTL plants
is opening up opportunities to reduce risks and on
the same time for the use of natural gas in both
offshore and remote on-shore locations [4].
This challenge has been addressed by KT over the
past years in the framework of the R&D European
project “Innovative Catalytic Technologies &
Materials for Next Gas to Liquid Processes”, NEXT-
GTL, ended in October 2013. The development of
novel process schemes for the production of syngas
at lower temperature than the traditional ones,
without affecting natural gas conversion and saving
IndustrIal Plants - May 2014
24