Page 48 - Impiantistica industriale Luglio Agosto 20147
P. 48
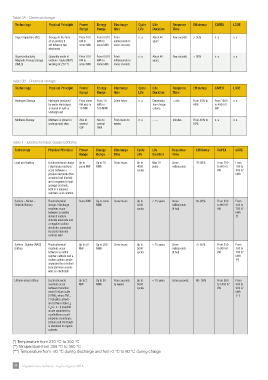
Table 3A - Electrical storage
technology Physical Principle Power energy Discharge cycle life response effciency caPeX lcoe
range range time life Duration time
Super Capacitors (SC) Storage in the form From 100 From 0.010 From n. a. About 40 Few seconds > 95% n. a. n. a.
of an electric f kW to kWh to milliseconds to years
eld between two some MW some kWh some seconds
electrodes
Superconductivity Generally made of From 100 From 0.010 From n. a. About 40 Few seconds > 95% n. a. n. a.
Magnetic Energy Storage niobium- titane (NbTi) kW to kWh to milliseconds to years
(SMES) working at 270 °C some MW some kWh some seconds
Table 3B - Chemical storage
technology Physical Principle Power energy Discharge cycle life response effciency caPeX lcoe
range range time life Duration time
Hydrogen Storage Hydrogen produced From some From 10 Some hours n. a. Depending < min From 20% to From 1500 n. a.
by water electrolysis kW also to kWh to from design 40% to 4000 €/
is stored in tank or 10 MW 100 MWh criteria kW
Underground
Methane Storage Methane is stored in Also to Also to From hours to n. a. ----- minutes From 40% to n. a. n. a.
underground sites several several weeks 50%
GW GWh
Table 4 - Electrochemical: classic batteries
technology Physical Principle Power energy Discharge cycle life response effciency caPeX lcoe
range range time life Duration time
Lead acid battery Electrochemical charge Up to Up to 10 Some hours Up to Max 10 Some 75-85% From 150 From
/ discharge reactions some MW MWh 4000 years milliseconds to 600 €/ 100 to
occur between a cycles kW 500 €/
positive electrode (that kWh
contains lead dioxide)
and a negative (a lead
spongy) electrode,
both in a aqueous
sulphuric acid solution
Sodium – Nickel – Electrochemical Some MW Up to some Some hours Up to < 15 years Some 85-90% From 300 From
Chloride Battery charge / discharge MWh 5000 milliseconds to 800 €/ 550 to
reactions occur cycles (if hot) kW 750 €/
between a positive kWh
nickel & sodium (*)
chloride electrode and
a negative sodium
electrode, separated
by a beta alumina
ceramic wall
Sodium- Sulphur (NA/S) Electrochemical Up to 50 Up to 500 Some hours Up to < 15 years Some 75-85% From 350 From
Battery reactions occur MW MWh 5000 milliseconds to 900 €/ 400 to
between a molten cycles (if hot) kW 700 €/
sulphur cathode and a kWh
molten sodium anode (**)
separated by a sodium
beta alumina ceramic
wall, as electrolyte
Lithium-iones battery Electrochemical Up to 2 Up to 50 From seconds Up to < 10 years Some seconds 80- 95% From 900 From
reactions occur MW MWh to weeks 5000 to 1800 €/ 400 to
between transition cycles kW 900 €/
metal Lithium oxide kWh
(LiTMO where TM = (***)
2
CO,Ni,Mn) cathode
and Lithium state Li x
C (o< x< l) graphite
6
anode separated by
a polietilene or poli-
propilene membrane.
Lithium salt electrolyte
is dissolved in organic
solvents.
(*) Temperature from 270 °C to 350 °C
(**) Temperature from 300 °C to 350 °C
(***) Temperature from -30 °C during discharge and from 0 °C to 60 °C during charge
44 Impiantistica Italiana - Luglio-Agosto 2014