Page 20 - Impiantistica Industriale
P. 20
TRANSPORT INFRASTRUCTURE
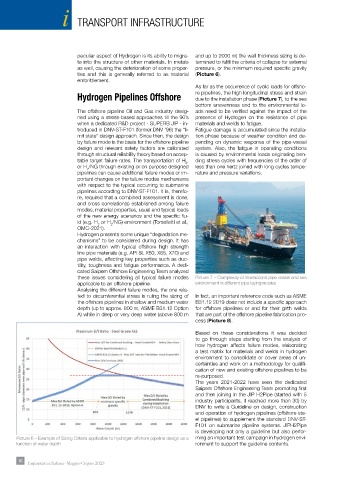
peculiar aspect of Hydrogen is its ability to migra- and up to 2000 m) the wall thickness sizing is de-
te into the structure of other materials. In metals termined to fulfil the criteria of collapse for external
as well, causing the deterioration of some proper- pressure, or the minimum required specific gravity
ties and this is generally referred to as material (Picture 6).
embrittlement.
As far as the occurrence of cyclic loads for offsho-
Hydrogen Pipelines Offshore re pipelines, the high longitudinal stress and strain
due to the installation phase (Picture 7), to the sea
bottom unevenness and to the environmental lo-
The offshore pipeline Oil and Gas industry desig- ads need to be verified against the impact of the
ned using a stress-based approaches till the 90’s presence of Hydrogen on the resistance of pipe
when a dedicated R&D project - SUPERB JIP - in- materials and welds to fatigue.
troduced in DNV-ST-F101 (former DNV ’96) the “li- Fatigue damage is accumulated since the installa-
mit state” design approach. Since then, the design tion phase because of weather condition and de-
by failure mode is the basis for the offshore pipeline pending on dynamic response of the pipe-vessel
design and relevant safety factors are calibrated system. Also, the fatigue in operating conditions
through structural reliability theory based on accep- is caused by environmental loads originating ben-
table target failure rates. The transportation of H , ding stress cycles with frequencies of the order of
2
or H /NG through existing or on purpose designed less than one hertz joined with long cycles tempe-
2
pipelines can cause additional failure modes or im- rature and pressure variations.
portant changes on the failure modes mechanisms
with respect to the typical occurring to submarine
pipelines according to DNV-ST-F101. It is, therefo-
re, required that a combined assessment is done,
and cross correlation(s) established among failure
modes, material properties, usual and typical loads
of the new energy scenarios and the specific flu-
id (e.g. H or H /NG) environment (Torselletti et al.,
2
2
OMC-2021).
Hydrogen presents some unique “degradation me-
chanisms” to be considered during design. It has
an interaction with typical offshore high strength
line pipe materials (e.g. API 5L X60, X65, X70) and
pipe welds, affecting key properties such as duc-
tility, toughness and fatigue performance. A dedi-
cated Saipem Offshore Engineering Team analyzed
these issues considering all typical failure modes Picture 7 – Complexity of interactions pipe vessel and sea
applicable to an offshore pipeline. environment in different pipe laying modes
Analysing the different failure modes, the one rela-
ted to circumferential stress is ruling the sizing of In fact, an important reference code such as ASME
the offshore pipelines in shallow and medium water B31.12 2019 does not include a specific approach
depth (up to approx. 800 m, ASME B31.12 Option for offshore pipelines or and for their girth welds
A) while in deep or very deep water (above 800 m that are part of the offshore pipeline fabrication pro-
cess (Picture 8).
Based on these considerations it was decided
to go through steps starting from the analysis of
how hydrogen affects failure modes, elaborating
a test matrix for materials and welds in hydrogen
environment to consolidate or cover areas of un-
certainties and work on a methodology for qualifi-
cation of new and existing offshore pipelines to be
re-purposed.
The years 2021-2022 have seen the dedicated
Saipem Offshore Engineering Team promoting first
and then joining in the JIP H2Pipe (started with 5
industry participants, it reached more than 30) by
DNV to write a Guideline on design, construction
and operation of hydrogen pipelines (offshore ste-
el pipelines) to supplement the standard DNV-ST-
F101 on submarine pipeline systems. JIPH2Pipe
is developing not only a guideline but also perfor-
Picture 6 – Example of Sizing Criteria applicable to hydrogen offshore pipeline design as a ming an important test campaign in hydrogen envi-
function of water depth ronment to support the guideline contents.
16 Impiantistica Italiana - Maggio-Giugno 2023