Page 107 - Impiantistica industriale
P. 107
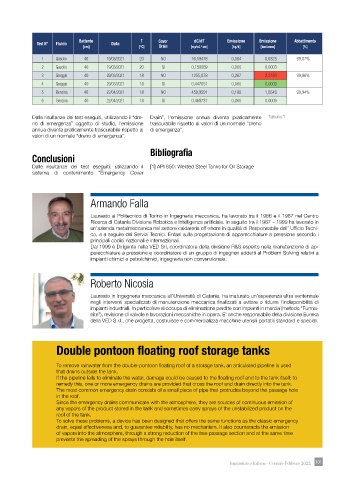
Battente T Cover dC/dT Emissione Emissione Abbattimento
Test N° Fluido Data
[cm] [°C] Drain [mg/m3 * sec] [kg/h] [ton/anno] [%]
1 Gasolio 40 19/03/2021 20 NO 16,19478 0,004 0,0325 99,07%
2 Gasolio 40 19/03/2021 20 SI 0,150069 0,000 0,0003
3 Greggio 40 29/03/2021 18 NO 1255,078 0,287 2,5180 99,96%
4 Greggio 40 29/03/2021 18 SI 0,447051 0,000 0,0009
5 Benzina 40 22/04/2021 18 NO 459,9591 0,189 1,6549 99,94%
6 Benzina 40 22/04/2021 18 SI 0,468737 0,000 0,0009
Dalle risultanze dei test eseguiti, utilizzando il “dre- Drain”, l’emissione annua diventa praticamente Tabella 1
no di emergenza” oggetto di studio, l’emissione trascurabile rispetto ai valori di un normale “dreno
annua diventa praticamente trascurabile rispetto ai di emergenza”.
valori di un normale “dreno di emergenza”.
Bibliografia
Conclusioni
Dalle risultanze dei test eseguiti, utilizzando il [1] API 650: Welded Steel Tanks for Oil Storage
sistema di contenimento “Emergency Cover
Armando Falla
Laureato al Politecnico di Torino in Ingegneria meccanica, ha lavorato tra il 1986 e il 1987 nel Centro
Ricerca di Catania Divisione Robotica e Intelligenza artificiale. In seguito tra il 1987 – 1999 ha lavorato in
un’azienda metalmeccanica nel settore caldareria off-shore in qualità di Responsabile dell’ Ufficio Tecni-
co, e a seguire dei Servizi Tecnici. Enfasi sulla progettazione di apparecchiature a pressione secondo i
principali codici nazionali e internazionali.
Dal 1999 è Dirigente nella VED Srl, coordinatore della divisione R&S esperto nella manutenzione di ap-
parecchiature a pressione e coordinatore di un gruppo di ingegneri addetti al Problem Solving relativi a
impianti chimici e petrolchimici, ingegneria non convenzionale.
Roberto Nicosia
Laureato in Ingegneria meccanica all’Università di Catania, ha maturato un’esperienza ultra ventennale
negli interventi specializzati di manutenzione meccanica finalizzati a evitare o ridurre l’indisponibilità di
impianti industriali. In particolare si occupa di eliminazione perdite con impianti in marcia (metodo “Furma-
nite”), revisione di valvole e lavorazioni meccaniche in opera. E’ anche responsabile della divisione Eureka
della VED S.r.l., che progetta, costruisce e commercializza macchine utensili portatili standard e speciali.
Double pontoon floating roof storage tanks
To remove rainwater from the double-pontoon floating roof of a storage tank, an articulated pipeline is used
that drains outside the tank.
If the pipeline fails to eliminate the water, damage could be caused to the floating roof and to the tank itself: to
remedy this, one or more emergency drains are provided that cross the roof and drain directly into the tank.
The most common emergency drain consists of a small piece of pipe that protrudes beyond the passage hole
in the roof.
Since the emergency drains communicate with the atmosphere, they are sources of continuous emission of
any vapors of the product stored in the tank and sometimes carry sprays of the unstabilized product on the
roof of the tank.
To solve these problems, a device has been designed that offers the same functions as the classic emergency
drain, equal effectiveness and, to guarantee reliability, has no mechanism. It also counteracts the emission
of vapors into the atmosphere, through a strong reduction of the free passage section and at the same time
prevents the spreading of the sprays through the hole itself.
101
Impiantistica Italiana - Gennaio-Febbraio 2022 101