Page 68 - Impiantistica Italiana
P. 68
Moreover, high system footprint/volume and 2. Vacuum towers based
weight may limit its utilization in an offshore ap- project
plication where compactness and lightness are
required from the plant. The reference executed project was an offshore
On the other side, in the last years membrane seawater injection treatment plant operating in
deaeration is gaining relevance as an attractive the Baltic Sea with an overall design flow rate
alternative to the vacuum tower for degassing of 92.5 m /h coming from pretreatment system.
3
of injection seawater. This technology has been The package included seawater treatments for
already tested in the field of seawater injection: the removal of both solid particles (required
different pilot scale plants have been built in outlet solid particles concentration: 0.1 ppm) and
order to evaluate the performances in oxygen dissolved oxygen (request outlet concentration:
removal and to optimize the most suitable sea- < 20 ppb) from seawater in order to avoid
water pretreatments upstream of membrane environmental alteration of the wells during
deaeration. injection.
Currently membrane deaeration is already suc- Feed water characteristics and treated water
cessfully used in many applications such as elec- requirements can be found in Table 1.
tronics, boiler feed water and food industries. A first seawater treatment was carried out by
The aim of the present work is to make a com- means of two fine filters, where solid particles
parison between vacuum towers and membra- with a diameter 2 µm and larger were removed
ne deaeration in seawater offshore applications. with an efficiency of 98%.
In details, the comparison was made between Each filter was composed by two different
an executed offshore project, where the seawa- granular media layers: the anthracite as the upper
ter deaeration was operated by a two stages one and garnet as lower layer. Polyelectrolyte
vacuum tower and the simulated equivalent and coagulant were dosed in the seawater
project obtained at the same operating condi- (downstream the injection feeding pumps) in
tions and performances, by replacing the exi- order to facilitate the precipitation of carry over
sting vacuum tower with membrane deaeration particles.
modules. During normal operation both filters were in
The comparative analysis was carried out in operation while in case of high pressure across
terms of process performances, economical the filters, the backwashing/regeneration phase
aspects (CAPEX and OPEX) and general cha- was required. Each filter was design to treat the
racteristics of the two degassing systems such 100% of the inlet flow rate so that backwashing/
as the equipment weight, the footprint/volume regeneration sequence was performed on both
and the amount of consumables and/or chemi- the filters sequentially.
cals consumed during operation. After being filtrated, the seawater was fed
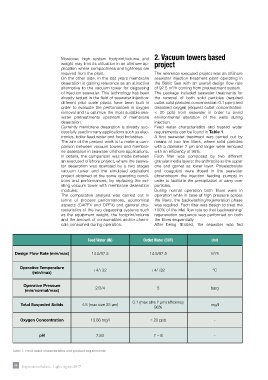
Feed Water (IN) Outlet Water (OUT) Unit
Design Flow Rate (min/max) 14.5/92.5 14.5/92.5 m /h
3
Operative Temperature
(min/max) +4/+32 +4/+32 °C
Operative Pressure 2/3/4 5 barg
(min/normal/max)
0.1 (max size 2 µm) efficiency
Total Suspeded Solids 4.5 (max size 25 µm) mg/l
98%
Oxygen Concentration 13.88 mg/l ≤ 20 ppb -
pH 7.83 7 – 8 -
Table 1. Feed water characteristics and product requirements
66 Impiantistica Italiana - Luglio-Agosto 2017