Page 29 - 60
P. 29
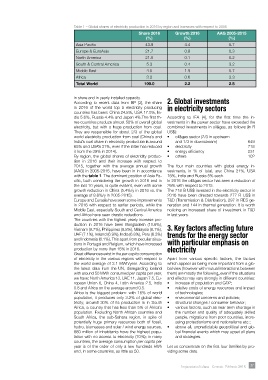
Table 1 – Global shares of electricity production in 2016 by region and increases with respect to 2005
Share 2016 Growth 2016 AAG 2005-2015
(%) (%) (%)
Asia Pacific 43.9 4.4 5.7
Europe & EuroAsia 21.7 0.8 0.3
North America 21.5 0.1 0.2
South & Central America 5.3 0.4 3.2
Middle East 4.5 1.9 5.7
Africa 3.2 0.6 3.3
Total World 100.0 2.2 2.8
in share and in yearly installed capacity.
According to recent data from BP [3], the share 2. Global investments
in 2016 of the world top 5 electricity producing in electricity sectors
countries has been: China 24.8%, USA 17.5%, In-
dia 5.6%, Russia 4.4% and Japan 4%.The first th- According to IEA [4], for the first time the in-
ree countries produce almost 50% of overall global vestments in the power sector have exceeded the
electricity, but with a huge production from coal. combined investments in oil&gas, as follows (in B
They are responsible for about 2/3 of the global US$):
world electricity production from coal (China’s and • oil&gas sector (2/3 in upstream
India’s coal share in electricity production is around and 1/3 in downstream) 649
65% and USA’s 31%, even if the latter has reduced • electricity 718
it from the 39% in 2014). • energy efficiency 231
By region, the global shares of electricity produc- • others 102
tion in 2016 and their increase with respect to
2015, together with the average annual growth The four main countries with global energy in-
(AAG) in 2005-2015, have been in in accordance vestments, in % of total, are: China 21%, USA
with the table 1. The dominant position of Asia Pa- 16%, India and Russia 5% each.
cific, both considering the growth in 2016 and in In 2016 the oil&gas sector has seen a reduction of
the last 10 years, is quite evident, even with some 26% with respect to 2015.
growth reduction in China (5.4%/y in 2016 vs. the The 718 B US$ invested in the electricity sector in
average of 8.8%/y in 2005-2015). 2016 have been directed towards 277 B US$ in
Europe and Eurasia have seen some improvements T&D (Transmission & Distribution), 297 in RES ge-
in 2016 with respect to earlier periods, while the neration and 144 in thermal generation. It is worth
Middle East, especially South and Central America noticing an increased share of investment in T&D
and Africa have seen drastic reductions. in last years.
The countries with the highest yearly increase pro-
duction in 2016 have been Bangladesh (10.6%),
Vietnam (9.7%), Philippines (8.8%), Malaysia (8.1%), 3. Key factors affecting future
UAE (7.1%), Ireland (6.9%), India (6.8%), Peru (6.3%) trends for the energy sector
and Indonesia (6.1%). This apart from peculiar situa-
tions in Portugal and Belgium, which have increased with particular emphasis on
production by more than 15% in 2016. electricity
Great differences exist in the per capita consumption
of electricity in the various regions with respect to Apart from various specific factors, the factors
the world average of 3.1 MWh/year. According to which appear as being more important from a glo-
the latest data from the UN, disregarding Iceland bal view (however with mutual interactions between
with around 50 MWh consumed per capita per year, them) are mostly the following, even if the situations
we have: North America 13, UAE 11, Japan 7.5, Eu- and effects may vary strongly in different countries:
ropean Union 6, China 4, Latin America 2.5, India • increase of population and GDP;
0.8 and Africa on the average around 0.5. • relative costs of energy resources and impact
Africa is the biggest problem: with 16% of world of technologies;
population, it produces only 3.2% of global elec- • environmental concerns and policies;
tricity; around 30% of its production is in South • structural changes / consumer behavior;
Africa, a country that has less than 5% of Africa’s • various factors, such as near term shortage in
population. Excluding North African countries and the number and quality of adequately skilled
South Africa, the sub-Sahara region, in spite of people, migrations from poor countries, incre-
potentially huge primary resources both of fossil, asing protectionisms and nationalisms etc.;
hydro, biomasses and solar / wind energy sources, • above all, unpredictable geopolitical and glo-
880 million of inhabitants have the highest popu- bal financial events which may upset all plans
lation with no access to electricity (70%); in many and strategies.
countries, the average consumption per capita per
year is of the order of only a few hundreds kWh Let us concentrate on the first four families by pro-
and, in some countries, as little as 50. viding some data.
Impiantistica Italiana - Gennaio- Febbraio 2018 27