Page 27 - 60
P. 27
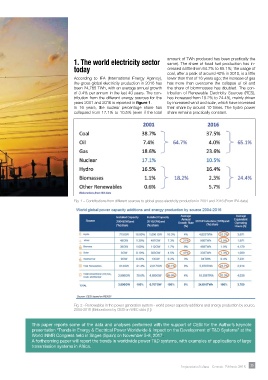
1. The world electricity sector amount of TWh produced has been practically the
same). The share of fossil fuel production has in-
today creased a little from 64.7% to 65.1%; the usage of
coal, after a peak of around 42% in 2010, is a little
According to IEA (International Energy Agency), lower than that of 16 years ago; the increase of gas
the gross global electricity production in 2016 has has more than overcome the collapse of oil and
been 24,765 TWh, with an average annual growth the share of biommasses has doubled. The con-
of 3.4% per annum in the last 40 years. The con- tribution of Renewable Electricity Sources (RES),
tribution from the different energy sources for the has increased from 18.2% to 24.4%, mainly driven
years 2001 and 2016 is reported in figure 1. by increased wind and solar, which have increased
In 16 years, the nuclear percentage share has their share by around 10 times. The hydro power
collapsed from 17.1% to 10.5% (even if the total share remains practically constant.
Fig. 1 – Contributions from different sources to global gross electricity production in 2001 and 2016 (From IEA data)
Fig. 2 - Renewables in the power generation system - world power capacity additions and energy production by source,
2004-2016 (Elaborations by CESI on WEC data [1])
This paper reports some of the data and analyses performed with the support of CESI for the Author’s keynote
presentation “Trends in Energy & Electrical Power Worldwide & Impact on the Development of T&D Systems” at the
World INMR Congress held in Sitges (Spain) on November 5-8, 2017.
A forthcoming paper will report the trends in worldwide power T&D systems, with examples of applications of large
transmission systems in Africa.
Impiantistica Italiana - Gennaio- Febbraio 2018 25