Page 31 - Impiantistica industriale
P. 31
century, multistage global pandemic has caused an
estimated 25 million deaths, increased global public
debt by 28 percent to 256 percent of GDP, shrunk
global GDP by 3.3 percent, and given rise to rapidly
increasing inflation across the globe. Supply chains
were under significant strain, energy markets were
already tight, and global commodity prices had ris-
en to ten-year highs. The war in Ukraine has exac-
erbated all these trends, affecting lives and liveli-
hoods both locally and globally and threatening the
most vulnerable with the potential for a marked de-
cline in energy and food security and affordability.
At the same time, the manifestations of climate
change—among them unprecedented heat waves
in India and worsening drought in the Ameri-
can West—continued to multiply. In that context,
the Sixth assessment report, published by the
United Nation’s Intergovernmental Panel on Cli-
mate Change, issued a few days after the invasion
provided a stark warning that climate change was
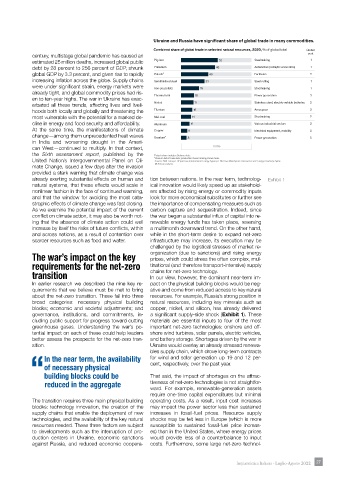
already exerting substantial effects on human and tion between nations. In the near term, technolog- Exhibit 1
natural systems, that these effects would scale in ical innovation would likely speed up as stakehold-
nonlinear fashion in the face of continued warming, ers affected by rising energy or commodity inputs
and that the window for avoiding the most cata- look for more economical substitutes or further see
strophic effects of climate change was fast closing. the importance of compensating measures such as
As we examine the potential impact of the current carbon capture and sequestration. Indeed, since
conflict on climate action, it may also be worth not- the war began a substantial influx of capital into re-
ing that the absence of climate action could well newable energy funds has taken place, reversing
increase by itself the risks of future conflicts, within a multimonth downward trend. On the other hand,
and across nations, as a result of contention over while in the short-term desire to expand net-zero
scarcer resources such as food and water. infrastructure may increase, its execution may be
challenged by the logistical stresses of market re-
The war’s impact on the key organization (due to sanctions) and rising energy
prices, which could stress the often complex, mul-
requirements for the net-zero tinational (and therefore transport-intensive) supply
transition chains for net-zero technology.
In our view, however, the dominant near-term im-
In earlier research we described the nine key re- pact on the physical building blocks would be neg-
quirements that we believe must be met to bring ative and come from reduced access to key natural
about the net-zero transition. These fall into three resources. For example, Russia’s strong position in
broad categories: necessary physical building natural resources, including key minerals such as
blocks; economic and societal adjustments; and copper, nickel, and silicon, has already delivered
governance, institutions, and commitments, in- a significant supply-side shock (Exhibit 1). These
cluding public support for progress toward cutting materials are essential inputs to four of the most
greenhouse gases. Understanding the war’s po- important net-zero technologies: onshore and off-
tential impact on each of these could help leaders shore wind turbines, solar panels, electric vehicles,
better assess the prospects for the net-zero tran- and battery storage. Shortages driven by the war in
sition. Ukraine would overlay an already stressed renewa-
bles supply chain, which drove long-term contracts
In the near term, the availability for wind and solar generation up 19 and 12 per-
of necessary physical cent, respectively, over the past year.
“building blocks could be That said, the impact of shortages on the attrac-
reduced in the aggregate tiveness of net-zero technologies is not straightfor-
ward. For example, renewable-generation assets
require one-time capital expenditures but minimal
The transition requires three main physical building operating costs. As a result, input cost increases
blocks: technology innovation, the creation of the may impact the power sector less than sustained
supply chains that enable the deployment of new increases in fossil-fuel prices. Resource supply
technologies, and the availability of the key natural shocks may be felt less in Europe (which is more
resources needed. These three factors are subject susceptible to sustained fossil-fuel price increas-
to developments such as the interruption of pro- es) than in the United States, where energy prices
duction centers in Ukraine, economic sanctions would provide less of a counterbalance to input
against Russia, and reduced economic coopera- costs. Furthermore, some large net-zero technol-
Impiantistica Italiana - Luglio-Agosto 2022 27 27