Page 77 - Impiantistica industriale
P. 77
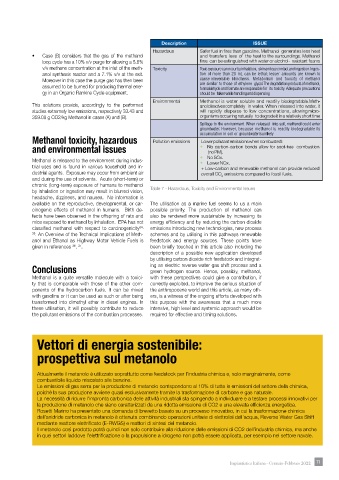
Description ISSUE
Hazardous Safer fuel in fires than gasoline. Methanol generates less heat
• Case (B) considers that the gas of the methanol and transfers less of the heat to the surroundings. Methanol
loop cycle has a 10% v/v purge for allowing a 5.6% fires can be extinguished with water or alcohol- resistant foams
v/v methane concentration at the inlet of the meth- Toxicity Toxic exposure can occur by inhalation, skin and eye contact and ingestion. Inges-
anol synthesis reactor and a 7.1% v/v at the exit. tion of more than 20 mL can be lethal; lesser amounts are known to
Moreover in this case the purge gas has then been cause irreversible blindness. Metabolism and toxicity of methanol
assumed to be burned for producing thermal ener- are similar to those of ethylene glycol. The degradation products of methanol,
formaldehyde and formate are responsible for its toxicity. Adequate precautions
gy in an Organic Rankine Cycle equipment. should be taken while handling and dispensing
Environmental Methanol is water soluble and readily biodegradable. Meth-
This solutions provide, accordingly to the performed anol dissolves completely in water. When released into water, it
studies extremely low emissions, respectively 33.43 and will rapidly disperse to low concentrations, allowing micro-
359.08 g CO2/kg Methanol in cases (A) and (B). organisms occurring naturally to degrade it in a relatively short time
Spillage to the environment. When released into soil, methanol could enter
groundwater. However, because methanol is readily biodegradable its
accumulation in soil or groundwater is unlikely
Methanol toxicity, hazardous Pollution emissions Lower pollutant emissions when combusted:
and environmental issues + No carbon-carbon bonds allow for soot-free combustion
(no PM).
+ No SOx.
Methanol is released to the environment during indus- + Lower NOx.
trial uses and is found in various household and in- + Low-carbon and renewable methanol can provide reduced
dustrial agents. Exposure may occur from ambient air overall CO emissions compared to fossil fuels.
and during the use of solvents. Acute (short-term) or 2
chronic (long-term) exposure of humans to methanol
by inhalation or ingestion may result in blurred vision, Table 7 - Hazardous, Toxicity and Environmental Issues
headache, dizziness, and nausea. No information is
available on the reproductive, developmental, or car- The utilisation as a marine fuel seems to us a main
cinogenic effects of methanol in humans. Birth de- possible priority. The production of methanol can
fects have been observed in the offspring of rats and also be rendered more sustainable by increasing its
mice exposed to methanol by inhalation. EPA has not energy efficiency and by reducing the carbon dioxide
classified methanol with respect to carcinogenicity 34, emissions introducing new technologies, new process
35 . An Overview of the Technical Implications of Meth- schemes and by utilising in this pathways renewable
anol and Ethanol as Highway Motor Vehicle Fuels is feedstock and energy sources. These points have
given in references , . been briefly touched in this article also including the
36 37
description of a possible new application developed
by utilising carbon dioxide rich feedstock and integrat-
Conclusions ing an electric reverse water gas shift process and a
green hydrogen source. Hence, possibly, methanol,
Methanol is a quite versatile molecule with a toxici- with these perspectives could give a contribution, if
ty that is comparable with those of the other com- correctly exploited, to improve the serious situation of
ponents of the hydrocarbon fuels. It can be mixed the anthropocene world and this article, as many oth-
with gasoline or it can be used as such or after being ers, is a witness of the ongoing efforts developed with
transformed into dimethyl ether in diesel engines. In this purpose with the awareness that a much more
these utilisation, it will possibly contribute to reduce intensive, high level and systemic approach would be
the pollutant emissions of the combustion processes. required for effective and timing solutions.
Vettori di energia sostenibile:
prospettiva sul metanolo
Attualmente il metanolo è utilizzato soprattutto come feedstock per l’industria chimica e, solo marginalmente, come
combustibile liquido miscelato alle benzine.
Le emissioni di gas serra per la produzione di metanolo corrispondono al 10% di tutte le emissioni del settore della chimica,
poiché la sua produzione avviene quasi esclusivamente tramite la trasformazione di carbone e gas naturale.
La necessità di ridurre l’impronta carbonica delle attività industriali sta spingendo a individuare e a testare processi innovativi per
la produzione di metanolo che siano caratterizzati da una ridotta emissione di CO2 e una elevata efficienza energetica.
Rosetti Marino ha presentato una domanda di brevetto basato su un processo innovativo, in cui la trasformazione chimica
dell’anidride carbonica in metanolo è ottenuta combinando operazioni unitarie di elettrolisi dell’acqua, Reverse Water Gas Shift
mediante reattore elettrificato (E-RWGS) e reattori di sintesi del metanolo.
Il metanolo così prodotto potrà quindi non solo contribuire alla riduzione delle emissioni di CO2 dell’industria chimica, ma anche
in quei settori laddove l’elettrificazione o la propulsione a idrogeno non potrà essere applicata, per esempio nel settore navale.
Impiantistica Italiana - Gennaio-Febbraio 2022 71 71