Page 53 - 85
P. 53
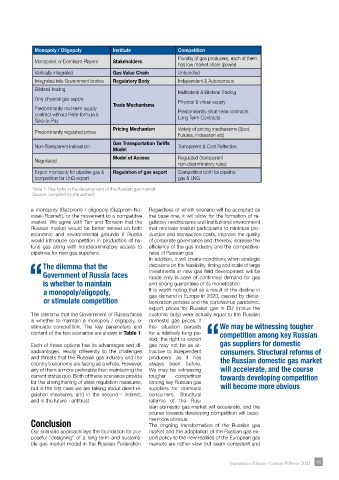
Monopoly / Oligopoly Institute Competition
Plurality of gas producers, each of them
Monopolist or Dominant Players Stakeholders
has low market share (power)
Vertically integrated Gas Value Chain Unbundled
Integrated into Government bodies Regulatory Body Independent & Autonomous
Bilateral trading
Multilateral & Bilateral Trading
Only physical gas supply Physical & virtual supply
Trade Mechanisms
Predominantly mid-term supply
contract without Price-formula & Predominantly short-term contracts
Take-or-Pay Long Term-Contracts
Pricing Mechanism Variety of pricing mechanisms (Spot,
Predominantly regulated prices
Futures, Indexation etc)
Gas Transportation Tariffs
Non-Transparent indexation Transparent & Cost Reflective
Model
Model of Access Regulated (transparent
Negotiated
non-discriminatory rules)
Export monopoly for pipeline gas & Regulation of gas export Competition both for pipeline
competition for LNG export gas & LNG
Table 1. Key forks in the development of the Russian gas market
Source: compiled by the authors
a monopoly (Gazprom) / oligopoly (Gazprom-No- Regardless of which scenario will be accepted as
vatek-Rosneft), or the movement to a competitive the base one, it will allow for the formation of re-
market. We agree with Tarr and Tomson that the gulatory mechanisms and institutional environment
Russian market would be better served on both that motivate market participants to minimize pro-
economic and environmental grounds if Russia duction and transaction costs, improve the quality
would introduce competition in production of na- of corporate governance and, thereby, increase the
tural gas along with nondiscriminatory access to efficiency of the gas industry and the competitive-
pipelines for new gas suppliers. ness of Russian gas.
In addition, it will create conditions when strategic
The dilemma that the decisions on the feasibility, timing and scale of large
Government of Russia faces investments in new gas field development will be
made only in case of confirmed demand for gas
“is whether to maintain and strong guarantees of its monetization.
a monopoly/oligopoly, It is worth noting that as a result of the decline in
gas demand in Europe in 2020, caused by decar-
or stimulate competition bonization policies and the coronavirus pandemic,
export prices for Russian gas in EU (minus the
The dilemma that the Government of Russia faces customs duty) were actually equal to the Russian
is whether to maintain a monopoly / oligopoly, or domestic gas prices. If
stimulate competition. The key parameters and this situation persists We may be witnessing tougher
content of the two scenarios are shown in Table 1. for a relatively long pe- competition among key Russian
riod, the right to export
Each of these options has its advantages and di- gas may not be as at-“gas suppliers for domestic
sadvantages, reacts differently to the challenges tractive to independent consumers. Structural reforms of
and threats that the Russian gas industry and the producers as it has the Russian domestic gas market
country’s economy are facing as a whole. However, always been before.
any of them is more preferable than maintaining the We may be witnessing will accelerate, and the course
current status quo. Both of these scenarios provide tougher competition towards developing competition
for the strengthening of state regulation measures, among key Russian gas
but in the first case we are talking about direct re- suppliers for domestic will become more obvious
gulation measures, and in the second - indirect, consumers. Structural
and in the future - antitrust. reforms of the Rus-
sian domestic gas market will accelerate, and the
course towards developing competition will beco-
Conclusion me more obvious.
The ongoing transformation of the Russian gas
Our scenario approach lays the foundation for pur- market and the adaptation of the Russian gas ex-
poseful “designing” of a long-term and sustaina- port policy to the new realities of the European gas
ble gas market model in the Russian Federation. markets are rather slow but seem consistent and
Impiantistica Italiana - Gennaio-Febbraio 2021 49 49